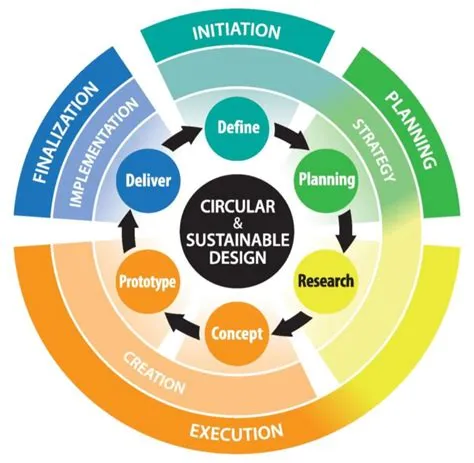
Hey there, design enthusiasts and sustainability champions! Ever wondered how we can create a world where innovation goes hand-in-hand with environmental responsibility? It’s a question that’s top of mind for many, and the answer, my friends, lies in the powerful synergy between design thinking and sustainability. This isn’t just about slapping a “green” label on existing products; it’s about fundamentally rethinking how we approach design, from conception to execution.
Design thinking, at its core, is a human-centered approach to problem-solving. It encourages empathy, experimentation, and iterative refinement. Think of it as a recipe for innovation, with ingredients like observation, ideation, prototyping, and testing. But what happens when we add a crucial ingredient – sustainability? The result is a potent blend that can revolutionize how we design products, services, and even entire systems.
The Marriage of Design Thinking and Sustainability
Integrating sustainability into design thinking isn’t a bolt-on; it’s a fundamental shift in perspective. Instead of solely focusing on functionality and aesthetics, we expand our lens to include environmental and social impacts. This means considering the entire lifecycle of a product – from raw material sourcing to disposal and everything in between. Are we using sustainable materials? Is the manufacturing process environmentally friendly? What’s the product’s end-of-life impact? These are the crucial questions we need to ask.
Imagine designing a chair, for instance. A traditional approach might focus on comfort, style, and cost. A sustainable design thinking approach, however, would also consider the source of the wood, the manufacturing processes’ energy consumption, the chair’s durability, and its recyclability or potential for biodegradation at the end of its life. It’s about creating a truly circular economy where waste is minimized and resources are maximized.
The Ideation Phase: Seeds of a Sustainable Future
The ideation phase, a crucial step in the design thinking process, is where the magic truly happens. It’s the brainstorming stage where we generate a plethora of ideas. When sustainability is front and center, this phase becomes a crucible for innovative, environmentally conscious solutions. We start by empathizing with users and understanding their needs, but we also consider the planet’s needs. This requires a deep understanding of environmental challenges and a commitment to finding solutions that benefit both people and the planet. This might involve exploring alternative materials, optimizing manufacturing processes for minimal waste, or designing for longevity and repairability.
For example, if you’re designing a new packaging solution, you might brainstorm ideas beyond conventional plastic. Could you utilize biodegradable materials? Perhaps you could explore innovative design to reduce packaging size and material usage. Could the packaging itself become part of the product experience or have a second life as something else entirely?
To enhance your ideation process, explore our comprehensive guide on design thinking ideation to unlock your team’s creative potential.
Prototyping and Testing: Putting Sustainability to the Test
Once you have a few promising ideas, it’s time to move into the prototyping phase. This is where you create tangible representations of your concepts, allowing you to test and refine them. In a sustainable design context, this might involve creating prototypes using recycled materials, or employing 3D printing to minimize material waste. The testing phase then becomes crucial for evaluating not only the functionality and usability of your design but also its environmental impact. This could involve life cycle assessments, analyzing the carbon footprint, or assessing the recyclability of materials.
For detailed insights into effective prototyping strategies, visit our blog on prototyping and testing. Learn how to transform your creative ideas into impactful solutions.
Collaboration and the Power of Shared Goals
Sustainability in design isn’t a solo endeavor. It requires collaboration between designers, engineers, manufacturers, and even consumers. Think of it like a complex ecosystem – each participant plays a crucial role. Collaborative ideation is essential to build a shared understanding of sustainability challenges and identify innovative solutions that work for everyone. By fostering open communication and shared responsibility, we can create truly sustainable designs.
The Principles of Sustainable Design Thinking
To truly succeed in incorporating sustainability, understanding the core principles of design thinking is vital. This involves embracing empathy, defining problems clearly, generating many ideas, prototyping rigorously, and testing extensively. But for sustainability, we add a crucial layer: considering the environmental and social impact at each step of the process. This requires a commitment to minimizing waste, conserving resources, and promoting ethical production practices. Think of it as adding a layer of ethical responsibility to the core design thinking framework.
Addressing Challenges: Overcoming Hurdles on the Path to Sustainability
Let’s be real; integrating sustainability isn’t always easy. It often comes with challenges. Sometimes, sustainable materials might be more expensive or less readily available. Manufacturing processes might need to be adapted, requiring time and investment. Consumer preferences might also need to shift towards sustainable products. But overcoming these challenges is precisely where the innovation within sustainable design thinking comes to the forefront. It’s about finding creative solutions, exploring innovative technologies, and educating consumers about the importance of sustainability.
Advanced Applications and Professional Development
The applications of sustainable design thinking are vast, ranging from product design to urban planning, architecture and even service design. Mastering these advanced concepts and techniques requires continuous professional development. Fortunately, there are abundant resources and opportunities available for learning and upskilling in this rapidly evolving field. Exploring topics like advanced applications, advanced concepts, and advanced techniques will be invaluable in your journey towards becoming a sustainability champion in design.
The Future is Green: Embracing a Sustainable Design Future
In conclusion, the integration of sustainability into design thinking is not just a trend; it’s a necessity. It’s a paradigm shift that demands a holistic approach, encompassing ethical considerations, environmental responsibility, and a commitment to creating a more sustainable future. By embracing empathy, collaboration, and iterative processes, we can unlock innovative solutions that benefit both humanity and the planet. It’s time we design for a better tomorrow – a future where sustainability and innovation walk hand-in-hand. Are you ready to be part of this revolution?
FAQs
Q1: How can I effectively integrate sustainability into my existing design projects?
A1: Start by auditing your current process. Identify areas where environmental impact is highest (material sourcing, manufacturing, transportation, disposal) and brainstorm alternatives. Consider using life cycle assessment tools to measure the environmental footprint of your design. Then, explore sustainable materials, processes, and packaging options. Prioritize repairability and recyclability.
Q2: What are some common challenges in implementing sustainable design thinking?
A2: Common challenges include higher upfront costs for sustainable materials, a lack of readily available sustainable alternatives, complexities in modifying existing manufacturing processes, and consumer resistance to higher prices for sustainable products. However, remember, long-term gains in reducing waste, energy use, and environmental impact often outweigh the upfront costs.
Q3: What resources are available for learning more about sustainable design thinking?
A3: Many online courses, workshops, and conferences focus on sustainable design. Organizations like the Ellen MacArthur Foundation and various universities offer programs. You can also find valuable information in books, journals, and industry publications. Don’t underestimate the power of online research and networking with professionals in the field.
Q4: How can I measure the success of a sustainable design project?
A4: Success can be measured in various ways, including reduced carbon footprint, decreased waste generation, improved resource efficiency, enhanced product lifespan, and increased consumer satisfaction with the sustainable aspects of the product. Use metrics like life cycle assessment (LCA) data, material usage reduction percentages, and waste diversion rates.
Q5: How can I encourage more sustainable practices within my organization?
A5: Start by advocating for a company-wide sustainability policy. Educate colleagues about sustainable design principles. Share case studies of successful sustainable projects. Participate in sustainability initiatives and encourage the adoption of eco-friendly practices across all departments. Lead by example and champion sustainable choices in your own work.