Hey there, innovators and idea enthusiasts! Ever felt stuck in a rut, struggling to find that breakthrough solution? You’re not alone. We all face those moments where creativity seems to vanish like a magician’s disappearing act. That’s where design thinking and ideation come in – powerful tools to unlock your creative potential and solve even the trickiest problems. Think of them as your secret weapons in the battle against the mundane!
This isn’t your grandma’s brainstorming session. Design thinking and ideation are dynamic processes, a blend of empathy, creativity, and practical application. It’s about understanding the human side of the problem, generating a whirlwind of ideas, and then meticulously refining them into something truly impactful. We’ll explore this exciting journey together, from the initial spark of an idea to the final polished product.
What is Design Thinking?
Imagine design thinking as a detective solving a case, except instead of catching criminals, you’re solving user problems. It’s a human-centered approach that focuses on understanding the needs and desires of the people you’re designing for. Forget simply building a product and hoping people like it. Design thinking puts the user at the heart of the process, ensuring the end result genuinely solves a problem and provides value.
This process typically involves five key stages:
1. Empathize: This is all about understanding your users. You immerse yourself in their world, observing their behaviours, conducting interviews, and analyzing their pain points. It’s like stepping into their shoes to truly understand their experiences.
2. Define: Once you’ve gathered all this valuable user information, it’s time to clearly define the problem. This often involves summarizing your findings into a concise problem statement that everyone can understand and agree on.
3. Ideate: This is where the magic happens! You unleash your inner creativity, brainstorming a wide range of potential solutions. Don’t worry about judging ideas at this stage; the goal is simply to generate as many possibilities as you can. We’ll delve deeper into ideation techniques later on.
4. Prototype: Before investing significant resources, you create rough prototypes—initial models or representations of your solution. This allows you to test your ideas quickly and cheaply, gathering valuable feedback to refine your design. Learn more about the importance of prototyping and testing on our blog.
5. Test: The final stage involves testing your prototype with real users. Observe how they interact with it, gather their feedback, and use this information to iterate and improve your design. This iterative process is crucial to ensuring your solution is truly effective and user-friendly.
The Power of Ideation: Where Ideas Take Flight
Ideation is the heart of design thinking – the phase where you generate creative solutions to your defined problem. Think of it as a mental explosion of possibilities, a brainstorming supernova! It’s about quantity over quality at this stage. The more ideas you generate, the greater your chance of finding a truly brilliant solution.
So, how do you unleash this creative potential? Here are a few powerful techniques:
Brainstorming: The classic technique! Gather a group, set a timer, and let the ideas flow freely. No idea is too wild or unrealistic at this stage.
Mind Mapping: Visually organize your thoughts using a central idea and branching out with related concepts. It’s a great way to explore connections and identify potential solutions you might otherwise overlook.
SCAMPER: A checklist that prompts you to think about how you can Substitute, Combine, Adapt, Modify, Put to other uses, Eliminate, and Reverse elements of your existing ideas.
Lateral Thinking: This involves challenging assumptions and looking at problems from different perspectives. Think outside the box – literally!
Role-Playing: Put yourself in the shoes of your users and brainstorm solutions from their perspective.
Collaborative Ideation: The Power of Teamwork
Innovation rarely happens in isolation. Effective ideation thrives in collaborative environments. When you bring together diverse perspectives and skill sets, you unlock a synergy that sparks truly innovative solutions. Collaborative ideation isn’t just about throwing ideas around; it’s about leveraging the unique strengths of each team member.
Think of a jazz band. Each musician plays their instrument, but the magic comes from their collective improvisation, their ability to respond and build upon each other’s contributions. Similarly, effective collaborative ideation requires active listening, respectful feedback, and a willingness to build upon the ideas of others.
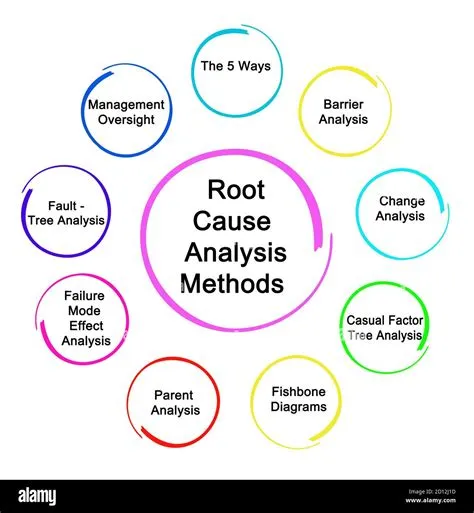
Root Cause Analysis: Getting to the Heart of the Matter
Often, before we can even begin the ideation process, we need to understand the root cause of the problem we’re trying to solve. Root cause analysis techniques are crucial for identifying the underlying issues driving a problem, not just its symptoms. Imagine treating a fever without addressing the underlying infection – you’re only dealing with the surface.
Several effective root cause analysis techniques exist, including the “5 Whys,” fishbone diagrams (Ishikawa diagrams), and fault tree analysis. These techniques help you peel back the layers of a problem, digging deeper until you uncover the core issue that needs addressing. This allows for a more focused and effective ideation process, ensuring you’re addressing the true problem, not just its superficial manifestations.
Moving Beyond Ideation: From Concept to Reality
Once you have a strong set of ideas, it’s time to move beyond the conceptual stage and bring your ideas to life. This involves prototyping, testing, and iterating—a continuous cycle of refinement based on user feedback. Remember, design thinking is an iterative process, not a linear one. It’s a journey, not a destination. Understanding the principles of design thinking is crucial to navigating this iterative path successfully.
Prototyping allows you to test your assumptions and gather valuable feedback early in the process, saving you time, money, and potential headaches down the road. From simple sketches and paper prototypes to more sophisticated digital models, the level of fidelity of your prototype should align with the stage of development.
Testing involves putting your prototypes in front of real users and observing how they interact with them. Their feedback is invaluable; it informs your design decisions and helps you identify areas that need improvement. We have a whole section dedicated to prototyping and testing techniques that you might find helpful.
The iterative nature of design thinking is what sets it apart from traditional linear approaches. It’s about continuous improvement, adapting and refining your design based on user feedback and data. By embracing this iterative process, you increase the chances of creating a solution that truly resonates with your users.
The Importance of Professional Development
In today’s rapidly evolving world, staying ahead of the curve is critical. Continuously improving your design thinking and ideation skills through professional development programs, workshops, and online resources is essential for remaining competitive and innovative. Many resources are available to help you enhance your skills, whether you prefer formal training or self-guided learning.
Conclusion
Design thinking and ideation are not just buzzwords; they’re powerful tools that can transform the way you approach problem-solving and innovation. By embracing a human-centered approach, fostering collaboration, and utilizing effective ideation techniques, you can unlock your creative potential and develop impactful solutions that truly make a difference. It’s about more than just coming up with ideas; it’s about understanding the “why” behind the problem, and translating that understanding into practical and effective solutions. So, go forth, unleash your creativity, and start designing a better future! Remember to check out our blog for more information on creative problem-solving and other related topics! And don’t forget to check out our resources on advanced techniques and applications in design thinking for more in-depth learning!
FAQs
1. What’s the difference between brainstorming and ideation? Brainstorming is a technique used during the ideation process. Ideation is the broader concept of generating ideas, while brainstorming is one method to achieve that.
2. Is design thinking only for designers? Absolutely not! Design thinking principles are applicable across all industries and professions. Anyone looking to solve problems creatively can benefit from it.
3. How long does the design thinking process typically take? It varies greatly depending on the complexity of the problem. Some projects might be completed in a few weeks, while others may take months.
4. What if my initial ideas don’t work out? That’s part of the process! Design thinking is iterative. You learn from failures, refine your approach, and continue iterating until you reach a successful solution.
5. Where can I find more resources on design thinking and ideation? Our blog at ideation.biz.id/blog offers a wealth of resources, articles, and insights into design thinking and ideation, covering various topics from foundations of design thinking to innovation workshops. You’ll also find helpful resources on tools and techniques, design thinking in practice, and more.