Hey there, fellow innovators! Ever felt stuck in a rut, staring at a blank page, desperately searching for that groundbreaking idea? You’re not alone. Many of us struggle with the initial spark, that moment of brilliance that ignites a project. But what if I told you there’s a powerful process, a proven methodology, that can help you unlock your creative potential and generate amazing solutions? That’s where design thinking and ideation step in – a dynamic duo that transforms challenges into opportunities.
Design thinking, at its core, is a human-centered approach to problem-solving. It’s less about following rigid rules and more about embracing a flexible, iterative process. Think of it as a journey, not a destination, with each step building upon the last. It’s a mindset that encourages empathy, experimentation, and collaboration. It’s about understanding the needs of the people you’re designing for, and then crafting solutions that truly resonate with them. It’s like baking a cake – you wouldn’t just throw all the ingredients together and hope for the best, would you? You follow a recipe, adapt as needed, and taste test along the way. Design thinking is similar; it’s a structured process with room for flexibility and improvisation.
Ideation, on the other hand, is the creative engine of design thinking. It’s the brainstorming phase, the moment where ideas are born, nurtured, and refined. It’s about generating a wide range of possibilities, even if they seem outlandish at first. Remember, the goal isn’t to come up with the perfect solution right away; it’s to explore as many avenues as possible, to cast a wide net and see what you catch. Think of it as a fishing expedition – you might not catch the biggest fish on your first cast, but with patience and persistence, you’ll eventually reel in something amazing.
The Stages of Design Thinking: A Guided Journey
Design thinking typically involves five distinct phases: Empathize, Define, Ideate, Prototype, and Test. Let’s explore each one:
1. Empathize: Understanding the Human Element
Before you even begin brainstorming solutions, you need to deeply understand the problem you’re trying to solve. This involves immersing yourself in the user’s world, understanding their needs, pain points, and motivations. This stage is all about empathy – putting yourself in their shoes and seeing the world through their eyes. Conduct user interviews, observe user behavior, and analyze existing data. The better you understand your users, the better equipped you’ll be to create solutions that truly meet their needs.
2. Define: Sharpening Your Focus
Once you have a good grasp of the user’s needs, it’s time to clearly define the problem you’re tackling. This involves summarizing your findings from the empathize stage into a concise problem statement. This statement should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART). Think of it as creating a roadmap – you can’t get to your destination without knowing where you’re going.
3. Ideate: Unleashing Your Creativity
This is where the magic happens! The ideation phase is all about generating a wide range of potential solutions. There are no bad ideas at this stage – the more ideas you generate, the better. Employ various brainstorming techniques, such as mind mapping, sketching, and role-playing. Encourage diverse perspectives and foster a collaborative environment. This stage is about quantity over quality, aiming to generate a large pool of ideas to choose from later.
4. Prototype: Bringing Ideas to Life
Prototyping is the process of creating tangible representations of your ideas. This could be anything from a rough sketch on a napkin to a fully functional digital mockup. The key is to create something you can test and iterate upon. Rapid prototyping methods are crucial here, allowing you to quickly test and refine your ideas without investing too much time or resources into each iteration. Learn more about efficient prototyping and testing strategies to accelerate your progress. By creating prototypes, you can gain valuable feedback and identify potential flaws early on, saving time and resources in the long run.
5. Test: Refining and Iterating
Testing your prototypes is critical to validating your ideas and identifying areas for improvement. Gather feedback from users and observe how they interact with your prototypes. Use this feedback to iterate on your designs and create even better solutions. Testing isn’t just a one-time event; it’s an ongoing process that should be incorporated throughout the design thinking process. Consider collaborative ideation and collaborative techniques for effective feedback gathering.
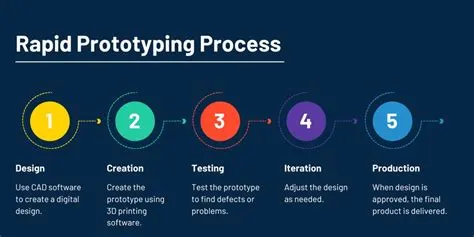
The Power of Rapid Prototyping
In today’s fast-paced world, speed is crucial. Rapid prototyping allows you to quickly build and test various iterations of your design, enabling faster feedback loops and accelerated innovation. Imagine trying to build a house without first creating a blueprint – it would be chaotic and inefficient. Rapid prototyping is like having that blueprint, allowing you to visualize your design and make changes before committing to a full-scale production. It’s about learning and adapting quickly; it’s a process of continuous improvement.
There are many different prototyping techniques available, from low-fidelity methods like paper prototypes to high-fidelity methods like interactive digital mockups. The choice of method will depend on the project’s complexity, resources, and timeframe. Explore prototyping in industries to find best practices. Understanding different testing methods is key to making the most of your prototypes.
Beyond the Basics: Advanced Applications
Design thinking and ideation aren’t just for product designers; they’re valuable tools across various industries and disciplines. From software development to marketing, from healthcare to education, these methods can help unlock innovation and solve complex problems. Dive deeper into advanced applications of design thinking and advanced concepts to expand your skillset. Explore the principles of design thinking to gain a comprehensive understanding of this powerful framework.
Furthermore, exploring advanced techniques in design thinking can significantly enhance your problem-solving capabilities. And don’t underestimate the power of innovation workshops – they can be invaluable for fostering collaborative ideation and accelerating the design thinking process. These workshops can help you hone your skills and learn from experienced practitioners.
Consider the impact of design thinking in practice and how it can reshape your approach to problem-solving. Even a simple understanding of foundations of design thinking can transform your perspective.
Finally, continuous professional development is key to staying ahead in this ever-evolving field. The more you learn and practice, the more effective you’ll become at applying design thinking and ideation in your work.
Conclusion
Design thinking and ideation are not just buzzwords; they’re powerful tools that can transform the way you approach problem-solving and innovation. By embracing a human-centered approach, fostering collaboration, and embracing iterative processes, you can unlock your creative potential and generate truly impactful solutions. Remember, the journey of innovation is a continuous process of learning, experimenting, and refining. So, go forth, embrace the power of design thinking, and let your creativity soar!
Frequently Asked Questions
- What is the difference between design thinking and ideation? Design thinking is a human-centered problem-solving methodology, while ideation is the specific phase within design thinking focused on generating creative solutions. Ideation is a crucial part of the design thinking process but not the entire process itself.
- Why is rapid prototyping important in design thinking? Rapid prototyping allows for quick testing and iteration of ideas, leading to faster feedback loops and improved designs. It helps avoid investing significant resources in solutions that may not be effective.
- Can design thinking be applied to any problem? Yes, the principles of design thinking are applicable to a wide range of problems across various industries and disciplines. Its human-centered focus makes it adaptable to diverse situations.
- What are some common tools and techniques used in ideation? Common ideation tools and techniques include brainstorming, mind mapping, sketching, role-playing, and using various visual aids to capture and organize ideas.
- How can I improve my design thinking skills? Continuous learning through workshops, online courses, and practical application are essential for improving design thinking skills. Actively seeking feedback and collaborating with others are also crucial aspects of improving.